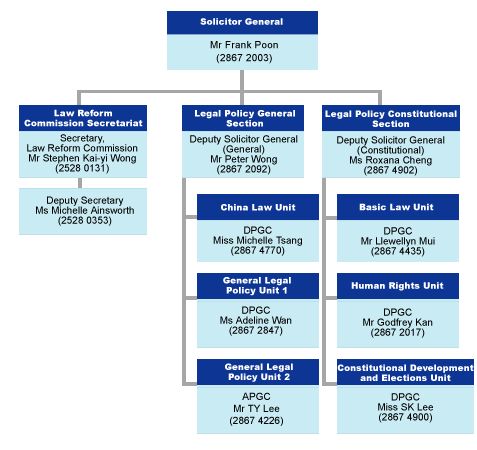
Organisation chart of the Legal Policy Division
2nd - 3rd floors, High block, QGO
Enquiries : 2867 2357
Fax : 2869 0670
The Legal Policy Division advises government departments and bureaus on whether proposed legislation, or a particular policy, is consistent with the Basic Law, international human rights standards, and established principles underlying the legal system. It also has a specialist unit that provides advice on (and promotes understanding of) the law on the Mainland. In addition, the division plays an active part in law reform, both through its responsibility for any new legislation promoted by the Secretary for Justice, and because the lawyers who serve in the Secretariat of the Law Reform Commission are part of the division.
General legal policy
As well as advising on the legality of policies established by the government, the division also assists in formulating policy, particularly in relation to the legal system and the legal profession. The division has assisted the legal profession in exploring the opportunities that China's accession to the World Trade Organization will offer and in enhancing its opportunities in the Mainland under the Closer Economic Partnership Arrangement (CEPA).
Where the Secretary for Justice has responsibility for a particular piece of new legislation, counsel in the division will take an active part in the preparation of the Bill and its presentation to the Executive and Legislative Councils. This will often include extensive consultation with those with an interest in the matter, both inside and outside the government.
Apart from preparing new legislation, the work of the division includes advising on:
- petitions from prisoners seeking remission of sentences or referral of their cases to the Court of Appeal
- public enquiries and complaints referred to the division
- petitions to the Chief Executive under Article 48(13) of the Basic Law
- statutory appeals to the Chief Executive or the Chief Executive in Council made by members of the public
- statutory appeals or representations from civil servants
The division is also responsible for advising the government on the powers and procedures of the Legislative Council.
Human right
The division provides specialised advice and assistance on human rights law within the Department of Justice and to other government bureaus and departments, reflecting the human rights provisions of the Basic Law. Apart from advising other divisions of the department on human rights law and issues arising from litigation, the division also advises government bureaus and departments on the human rights implications of legislative proposals and practices arising from the implementation of legislation to ensure their consistency with the human rights provisions of the Basic Law.
The division provides advice and assistance to government bureaus in the preparation of reports to the United Nations under various human rights instruments that have been extended to Hong Kong, namely the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (implemented by the Hong Kong Bill of Rights Ordinance (Cap 383)), the International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights, the Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women, the Convention on the Rights of the Child, the International Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Racial Discrimination, the Convention Against Torture and Other Cruel, Inhuman or Degrading Treatment or Punishment and the Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities. Counsel in the division also attend UN committee hearings on the HKSAR's periodic reports.
The division also advises government bureaus and departments extensively on the interpretation, implementation and implications of the Sex Discrimination Ordinance (Cap 480), the Disability Discrimination Ordinance (Cap 487), the Family Status Discrimination Ordinance (Cap 527) and the Race Discrimination Ordinance (Cap 602).
Mainland law and co-operation with the Mainland
Promoting Hong Kong's legal services in the Mainland and legal exchanges
The department continues to work closely with the legal profession in seeking greater access to the legal services market in the Mainland within the framework of CEPA and in promoting Hong Kong legal and arbitral services in the Mainland. In July 2010, the department, together with the Hong Kong legal and arbitration professional bodies, jointly organised a forum on Hong Kong legal services in Shanghai as part of Hong Kong's participation in the Shanghai Expo 2010. The forum showcased the strengths of Hong Kong as a legal and dispute resolution centre in the region.
In November 2010, the Secretary for Justice visited Guangzhou and Shenzhen and exchanged views with senior local government officials on fostering exchanges between the legal profession and co-operation on legal matters. In July 2011, the Secretary for Justice visited Beijing and discussed a range of matters with central government officials, including mutual legal assistance, the implementation of CEPA, the development of Hong Kong as a dispute resolution centre and co-operation with the legal profession.
The department continues to run programmes to facilitate Mainland officials' better understanding of Hong Kong's common law system. These include the Common Law Training Scheme, where participating Mainland officials attend an LLM programme either at the University of Hong Kong or the Chinese University of Hong Kong and undertake short-term attachments to different government departments or law-related organisations in Hong Kong for practical training. As at August 2011, a total of 165 Mainland officials had completed the training scheme.
Co-operation in cross-boundary legal matters
The department continues to provide assistance to policy bureaus and departments on legal issues arising from cross-boundary projects such as the construction of the Hong Kong – Zhuhai – Macao Bridge, the Guangzhou – Shenzhen – Hong Kong Express Rail Link and the development of the Lok Ma Chau Loop and Qianhai in Shenzhen.
Co-operation under the Framework Agreement
The Framework Agreement on Hong Kong/Guangdong Co-operation was signed in April 2010. The agreement seeks to promote greater co-operation between government organs and among legal professional bodies. It provides for the establishment of a communication mechanism on legal affairs and the strengthening of channels for the exchange of legal documents. It also encourages the legal and notarial professions to strengthen their co-operation. The department has discussed with Guangdong officials and the Hong Kong professional bodies ways to enhance exchanges and co-operation.
Co-operation on legal matters with Macao and Taiwan
In addition to pursuing closer legal co-operation with the Mainland, the department is also exploring ways to strengthen legal co-operation with our counterparts in Macao and Taiwan. The department has held preliminary discussions with the Macao SAR Government on an arrangement for the reciprocal enforcement of arbitral awards, along the lines of a similar arrangement that was concluded with the Mainland in 1999.
The department has begun considering ways to improve co-operation in legal affairs that would be mutually beneficial to Hong Kong and Taiwan. The department will explore ways to enhance legal co-operation in discussions with the relevant Taiwan authorities through the Hong Kong-Taiwan Economic and Cultural Co-operation and Promotion Council and the Taiwan-Hong Kong Economic and Cultural Co-operation Council.
Basic Law
The division provides advice to the government on the interpretation of the Basic Law, both in ensuring consistency of existing legislation with the Basic Law and in the formulation of new policies and legislation. Questions concerning the interpretation of provisions of the Basic Law have arisen in a number of important lawsuits. In such cases, counsel in the division work closely with other divisions in the preparation of the government's case, and provide advice and research on the Basic Law and other related issues.
The division plays a key role in promoting understanding of the Basic Law. It provides support to other government departments and public authorities including the Civil Service Training & Development Institute and the Civil Service Bureau both by providing counsel to give lectures and seminars on the Basic Law and by assisting in the production and revision of self-learning booklets and other training materials for use throughout the civil service. In 2011, the division (in conjunction with the Civil Service Training & Development Institute, the Civil Service Bureau and the Constitutional and Mainland Affairs Bureau) published one issue of the Basic Law Bulletin. The Bulletin was first published in 2001 and is intended to promote greater awareness and knowledge of the Basic Law among civil servants.
The division maintains a collection of research materials relevant to the Basic Law and constitutional law generally. This includes reference books and articles, relevant decisions and interpretations of the Standing Committee of the National People's Congress, reports of the Basic Law Consultative Committee and court judgments. The collection is regularly added to and updated as more case precedents and other literature on the Basic Law become available.
Constitutional Development and Elections
The division provides legal advice and support on constitutional development and electoral affairs to the relevant bureaux and departments. It advises the Electoral Affairs Commission (EAC), Constitutional and Mainland Affairs Bureau (CMAB), Registration and Electoral Office (REO) and Home Affairs Department (HAD) on the interpretation and application of the various pieces of election-related legislation.
The division also provides legal support on matters relating to post-election reviews, complaints and appeals, and where necessary, works with the relevant bureaux on the follow-up amendments to the relevant legislation.
Furthermore, the division assists the Administration to explain the legal aspects of the legislative proposals relating to constitutional development and electoral matters in the Executive Council, Legislative Council or any other committees, as required.